To Fight Sexual Assault and Harassment, Vessel Owners and Operators Must Comply with Heightened Reporting Requirements

In response to increased awareness of the prevalence of sexual assault and sexual harassment (SASH) in the maritime industry — and following a widely reported account by a U.S. Merchant Marine Academy cadet of sexual assault aboard a U.S.-flagged ship during her Sea Year training — Congress enacted into law the Safer Seas Act (SSA) in December 2022.Intended as a direct effort to prevent and punish SASH, the SSA, among other provisions:Requires the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) to revoke the license…
DAPI 101: Outreach and Enforcement
Even as the minimum Random Drug Testing Rate is raised to 50 PCT, the Coast Guard wants its mission to consist of 90% outreach and just 10% enforcement. Really.The domestic waterfront got some less-than-happy news when the U.S. Coast Guard announced that the calendar year 2019 minimum random drug testing rate had been set at 50 percent of covered crewmembers. It’s safe to say that nobody is happy about it, much less the Coast Guard itself.In truth, the Coast Guard had little to say about the matter. 46 CFR part 16.230(f)(2) requires the Commandant to set the minimum random drug testing rate at 50 percent when the positivity rate for drug use is greater than one percent.
Coast Guard Raises Minimum Random Drug Testing Rate to 50 PCT

The Coast Guard announced in the Federal Register that the calendar year 2019 minimum random drug testing rate is set at 50 percent of covered crewmembers. This rate is effective January 1, 2019 through December 31, 2019.The Coast Guard has increased the minimum random drug testing rate for 2019 as a result of Drug and Alcohol Management Information System (MIS) data for the most recent reporting year indicating that the positive rate is greater than one percent. 46 CFR part 16.230(f)(2)…
Safety and Preparation on the Brownwater Radar

Weather Channel Forecasters are predicting a “near-average” hurricane season for 2016, but warn that an average season does not mean businesses and residents shouldn’t prepare for the worst. While it is unclear whether the season, which began June 1, will bring about a few mild storms or a catastrophic Category 5 hurricane, one thing is for sure: safety and preparation are on the radars of the owners and operators of brownwater vessels. Although forecasters consider this year’s predicted 12 named storms “average”…
USCG Sets 2015 Drug Testing Rate
The Coast Guard set the calendar year 2015 minimum drug testing rate at 25 percent of covered crewmembers. The minimum random drug testing rate is effective January 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015. The Coast Guard requires marine employers to establish random drug testing programs for covered crewmembers on inspected and uninspected vessels. Every marine employer is required to collect and maintain a record of drug testing program data for each calendar year, and submit this data by March 15th of the following year to the Coast Guard in an annual Management Information System report.
Compatibility of CO2 Extinguisher Components

A recent marine casualty investigation of a shipboard fire onboard a U.S. flagged vessel in the Hampton Roads Captain of the Port (COTP) zone raised serious concerns with regards to carbon dioxide (CO2) fire extinguisher servicing. During shipboard fire-fighting operations a crewmember attempted to fight a fire using a 15lb CO2 extinguisher, but the extinguisher failed to properly discharge and only seeped from the neck of the extinguisher. The fire was eventually extinguished by another crewmember using a dry-chemical fire extinguisher. Following this shipboard fire, U.S.
Passenger Vessel Safety Record Defies NTSB Hit List
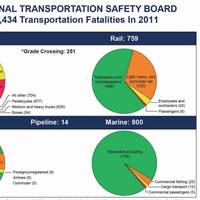
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) recently released its annual “Top 10 Most Wanted List” of Transportation Improvements for 2014. New this year was the issue of passenger vessel safety. Between 2000 and 2010, several accidents involving passenger vessels occurred. The domestic passenger vessel industry is highly regulated. Safety regulations for small passenger vessels took effect starting in 1996 for new construction, with phased implementation for existing vessels to be completed no later than March 2006.
USCG: Marijuana Use Unacceptable for Mariners

The U.S. Coast Guard issued a notice to ensure that mariners, marine employers, Medical Reviewing Officers and the public are knowledgeable of the continuing prohibition of marijuana use by those serving in safety-sensitive positions in the maritime transportation industry. The Coast Guard said it is important to note that marijuana remains a drug listed in Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. It remains unacceptable for any safety-sensitive employee serving in the maritime…
Ten Most Frequently Observed Towing Vessel Deficiencies
The U.S. Coast Guard’s Towing Vessel National Center of Expertise (NCOE) recently conducted an analysis of all deficiencies recorded by CG field personnel while Examining “uninspected towing vessels” (UTV) under the Towing Vessel Bridging Program and through other activities. The purpose of this analysis was to provide information and visibility on the most common UTV deficiencies list to share with UTV owner/operators in order to assist them in identifying and correcting common problems. In May of this year, they issued a comprehensive list that workboat operators – no matter what sector in which they operate – will find enormously helpful.
Crew System Integration on RHIBs and High Speed Craft

Human Systems Integration (HSI) is a recognized requirement for many organizations. This is rapidly becoming more important as the professional RHIB and high speed craft sector are required to perform increasingly complex tasks. The objective is for marine units to deal with new scenarios, make fast decisions and implement them using high speed craft and specialist equipment to achieve successful outcomes. Crew-Systems Integration (CSI) brings together all these elements for the fast boat sector.
Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010
On Friday, October 15, President Obama signed into law the Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010 (H.R. 3619). This is the first such authorization act for the Coast Guard since 2006. The statute is lengthy (128 pages) and addresses a wide variety of maritime issues. This article will attempt to identify those provisions expected to have the most impact or of the most interest. I have grouped these provisions into broad categories, although there is some natural overlap. The Coast Guard is provided specific authority to enforce the U.S. coastwise trade laws and its personnel are to be trained with regard to these laws. This provision is somewhat redundant, in that the agency, since its founding as the Revenue Cutter Service in 1790, has had this authority.
CG Launches Web-Based Credential Verification
The U.S. Coast Guard announced the launch of a new, Web-based tool to provide information on the validity of merchant mariner credentials. The Merchant Mariner Credential Verification tool was created following Operation Big Tow, a marine safety operation focused on ensuring uninspected towing vessels are being operated by properly licensed individuals. The operation identified the need for an open and rapid means of verifying the validity of merchant mariner credentials. The Merchant Mariner Credential Verification tool provides marine employers the means to ensure they are hiring mariners with valid credentials. It also allows Port State Control officers in foreign ports a real-time capability to verify U.S. mariners' credentials.
CG to Reduce Credentialing Process Time
The U.S. Coast Guard announced ongoing actions to reduce processing time for mariner credentials. The National Maritime Center, the Coast Guard's new centralized mariner credentialing processing facility in Martinsburg, W.Va., consolidated the Mariner Licensing and Documentation program that was performed in the 17 Regional Examination Centers throughout the nation approximately one year ago. The NMC receives mariners applications and conducts detailed evaluations to ensure the mariners' meet applicable requirements for the credentials sought. All mariners are evaluated in three areas including a professional qualification evaluation, a safety and security evaluation, and a medical evaluation.
Coast Guard Sets Minimum Random Drug Testing Rate
Due to results of random drug tests analyzed by the Coast Guard, RADM Paul Pluta has announced that the random drug testing rate will remain at 50 percent of covered crewmen in 2002. An evaluation of the 2000 Management Information System data collection forms submitted by marine employers determined that random drug testing on covered crewmen in 2000 resulted in positive test results 1.81 percent of the time. The minimum random drug testing rate is effective January 1, 2002 through December 31, 2002. Please note that 2001 MIS reports must be submitted no later than March 15, 2002. Source: PVA
USCG Looks for Invalid Licenses
Coast Guard Marine Safety Office (MSO) St. Louis is requesting the assistance of the marine industry, maritime unions, and individual mariners in helping to locate potentially invalid licenses issued from Regional Examination Center (REC) San Juan, Puerto Rico. The license certificates themselves may be representative of a variety of license transactions including original issues, renewals, duplicates and upgrades. The issuing port may be represented as San Juan, Puerto Rico, however, it may appear as another location. MSO St. Louis requests that marine employer's and maritime unions carefully scrutinize the license of their personnel to determine if any have licenses with these serial numbers.
Legal: Chemical Testing Following Serious Marine Acccident
Alcohol and drugs too frequently play a major role in maritime accidents. Subsequent to these accidents there are multiple problems involved in the collecting of specimens for testing the presence of alcohol or drugs in an individual's body. The Coast Guard has proposed several changes in the procedure for collecting those specimens. These proposed requirements would help to better understand and eventually avoid problems like the infamous Exxon Valdez accident of 1989, where the captain's blood alcohol content was .061% when finally taken eleven hours after the ship ran aground. Alcohol was also alleged to be a factor in the sinking of the Cape Fear off the coast of New England in 1999.
Lockout Halts Shipments At Vancouver
Shipments through Vancouver, Canada's busiest port, came to an almost complete halt as employers imposed a lockout on unionized longshore workers in a bid to force an end to a contract dispute. No talks are scheduled between the British Columbia Marine Employers Association and the unionized workers at the port of Vancouver, and federal officials have said the government has no immediate plans to force a settlement. The previous labor contract between employers and the International Longshore & Warehouse Union of Canada expired in 1998, and the two sides are at odds over several issues including wages and the use of non-union labor.
Random Drug Testing Rate Holds at 50 Percent
The USCG announced the minimum random drug testing rate for marine employers will remain at 50 percent of covered crew members for calendar year 2000. The USCG's decision to continue to present drug testing rate was based on analysis of the 1998 Management Information System (MIS) data collection forms submitted by marine employers, which showed random drug testing of vessel crew members resulted in positive test results 1.68 percent of the time. Federal regulations allow the USCG to reduce the random drug testing rate if MIS reports for the previous year show an industry-wide positive rate of less than one percent. Information on 1999 test results is due March 15, 2000.







