PODCAST: FMD & the Building of a Defense Juggernaut
You would be hard pressed to find a corporate leader more passionate about the company they lead; more dedicated to the customer they serve. In this case it’s George Whittier, CEO, Fairbanks Morse Defense and the U.S. Navy. Upon his return less than five years ago, Whittier has driven FMD towards the top of the U.S. Navy supply heap, with a string of strategic acquisitions. Whittier discusses with Maritime Matters: The Marinelink Podcast, FMD’s rich history and promising future in helping the U.S. Navy rebuild its strategic edge globally with a strengthened manufacturing base.
- George, let’s start out with your leadership at FMD. You originally joined Fairbanks Morse in 2009, you left in 2012, but you retook the helm in 2020. Why did you leave, and what drew you back?
When I left [in 2012], it was really just time to leave, things have a season. But at the time, I was sad about it: I loved this company, the products, the people, the market, and the opportunity to feel like I’m ‘serving.’
One of the biggest regrets in my life is that I didn’t serve. By doing the job I’m doing at Fairbanks Morse Defense, being such an integral supplier to the Navy and the Coast Guard, it’s given me [almost] that feeling of serving. [Compared to] the people in uniform, it’s not even close to the same thing; but for me it’s a way to give back.
So, I left the company, I went and I ran a couple other companies, and in December 2019 Fairbanks Morse was mainly an engine company, part of EnPro Industries, and they didn’t really know what to do with it. They decided to sell it into a private equity company called Arcline [which subsequently asked me to come back]. The day the transaction was announced in January of 2020, that was also my first day back to the company, and it’s been off to the races ever since.
- I must admit that the rapid expansion of FMD, via mergers and acquisitions starting in 2020, took me by surprise as one day I saw what was a diesel engine manufacturer, the next a burgeoning defense conglomerate. Can you talk a bit more about the strategy behind FMD’s growth?
That’s a great question, Greg. Go back to when Fairbanks Morse was part of the public company. I use the old phrase, ‘if all you have is a hammer every problem looks like a nail.’ At that point in time, we were an engine company [and the mantra to address challenges was] “Well, we just have to go sell more engines.”
With the acquisition by Arcline and [my return] we had a change of perspective.
We said “This actually isn’t an engine company, what we really are is a critical supplier to the Navy.”
With that as a guiding light, we said to ourselves, “Well, if we’re a critical supplier to the Navy, then we should be selling other critical equipment?”
That put us on the path of making these acquisitions, building the company to where we are today. So, with the Rolls Royce acquisition, that’s our 13th. It won’t close until sometime next year [2025], but that’s a pretty significant run in a four-year period of time.

Former Senator Alan Simpson had a great line: “If you have integrity, nothing else matters. If you don’t have integrity, nothing else matters.” That really resonated with me. -- George Whittier, CEO, FMD
- Can you tell me a little bit more about the integrity, velocity and teamwork mantra … what does that mean to you in real terms?
I like to do things in terms of threes, and I always tell people … “I’m not the smartest guy out there by any stretch, but I can remember three things.” So I figure if I can remember three things, then everyone else can remember three things, too.
It starts with integrity. Former Senator Alan Simpson had a great line. He said, “If you have integrity, nothing else matters. If you don’t have integrity, nothing else matters.”
That really resonated with me. I realized how important [integrity] is to me in how I run my life and how I do things, not just at work but in my personal life, too. We’re going to operate above board, we’re going to be honest, be respectful. We’re going to admit our mistakes, we’re going to fix problems when we have problems, we’re just going to be that good partner for our customers, our suppliers, and then our own teammates.
Then that feeds into teamwork. If you have integrity and you have that sense of honor and respect, and you operate in a sense of teamwork. A winning team is a team that works well together, a losing team is a team where you’re pointing fingers at each other and you’re placing blame all the time. We want a team that – we’re not going to win everything – but we’re going to win as a team and we’re going to lose as a team. And when we lose as a team, we’re going to figure out what we did wrong and then we’re going to fix it.
Because we have integrity. The second value, even though I talk about it third, is really the cornerstone for what we do here at Fairbanks Morse, and that’s velocity.
I tell folks that we have to be decisive in what we do, and I talk about velocity as speed with a direction. We will make decisions when we have 80% of the information that we need, and then we course correct, and we know that we’re going to make some mistakes because we’re operating with 80%, but because we have integrity and because we have teamwork, we can course correct, solve those problems and still get to the finish line, get to where we need to be before anyone else can get there. We’ve literally won projects where I’ve had a competitor call and tell me, and say, “You guys won that project before I knew there was a project.”
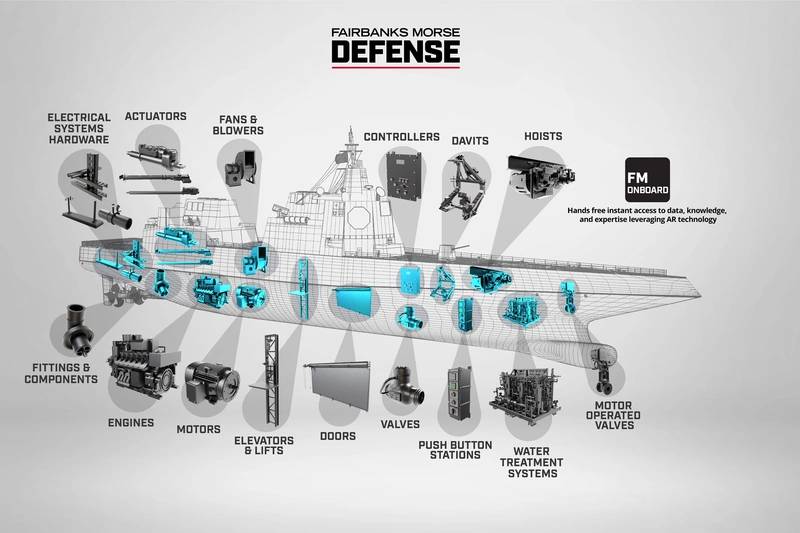 FMD has a growing portfolio of products on the ship + a growing tech base to service it for its life. Image courtesy FMD
FMD has a growing portfolio of products on the ship + a growing tech base to service it for its life. Image courtesy FMD
- I know you are passionate about the U.S. Navy industrial base. Can you summarize what you see today?
We’re in a dangerous world right now. Iran is shooting missiles at Israel, the Houthis are disrupting trade, everyone knows about Russia and Ukraine. And to me, the biggest challenge of all would be: what happens if China invades Taiwan? There’s some talk of that in a 2027 timeline, and in global timelines that’s tomorrow, and we’re not ready for that as a Navy. I get concerned when I see the shipbuilding budget for 2024, where the Navy [is decommissioning three times more ships than they’re building, including only six or seven newbuilds for 2025 when initially the projection was 10]. At a time when our Navy is shrinking, our industrial base is shrinking, we have a Chinese Navy that’s gone from 300 ships to 350 ships or greater.
The counter to that is always, ‘well, if you include all the allied nations we actually have a lot more ships, and the ships that we have are larger and more capable.’ I understand that, I really do, and I think we have the best Navy in the world, bar none. I don’t think that the Chinese can compete with us at all, but it is really concerning just on a sheer quantity of ships and the fact that [a potential Taiwan] conflict is right in their backyard, where for us its 6,000-8,000 miles away.
[When you see] the hundreds of thousands, millions of man-hours that we’re short to build the equipment that we need, it’s a concern for everybody.
So my passion on this is that we should be doing a lot more of this work in the Midwest. The biggest constraint today is labor. [The big navy yards are storying to subcontract] but I’d like to see that much more broadly.
A crazy idea I have is we ought to have a shipyard in St. Louis that’s making modules for all of the other shipyards, and you stick them on a barge and you sail them down the Mississippi River. There’s a lot of labor in the Heartland, and if you drive through the middle of the country, you see these rust belt towns where there’s labor available. There are tech schools, there’s trade schools, we can teach people how to weld. And then the shipyards that exist today really then should be transformed into assembly yards.
We don’t do that, and I think the main reason is because we don’t have enough demand [building six ships per year].
[The big Navy shipyards have] plenty of labor to do the work that they need to do today, but what’s it going to look like if we say “Hey, we have to build 25 to 30 ships a year.”
[To do that we have] to really transform the way that we do business today. And in order to do that, we’re going to need significantly more labor, we’re going to need more money from Congress. So, the Navy’s going to have to say, “Hey, instead of a $35 billion shipbuilding budget, it needs to be $40 to $45 billion.”
The Navy is our front line of defense; it’s freedom of the seas for everything that we want to do as a country. That has the follow on effect to the supply chain, the industrial base that then has to grow and be able to support that. And there’s tons of companies out there like, Fairbanks Morse, that are really waiting for that leadership. Now what we’re seeing is that there’s a lot of grassroots efforts [such as] a year ago I helped launch the Wisconsin Defense and Industry Coalition.
But none of that’s really going to be successful if we don’t start saying, ‘Contracts have to start coming out of the big yards, out of the big primes into the industrial base.’
And in order for that to happen, the big primes, the big shipyards, they have to have additional contracts so that they can manage their financials. Because they can’t just say, “Oh, all this stuff we’re doing today, we’re just going to outsource it.”
I’m really passionate about this topic, and [to be clear] I’m not trying to build ships just for the sake of building ships. I’m very concerned about the state of the world today. [Almost no one today] thinks of China right as a friendly country. I’ve been there about 20 times in my life, but I wouldn’t go today, it’s a very adversarial relationship there. It’d be great if we could try to simmer tensions a bit, but the way to do that is ‘peace through strength.’
- Perhaps a bit early, but when you think about the FMD legacy that you pass on, what would you like it to be?
I think there’s two things, Greg. If we go back in our [150-year] history, we made windmills, we made scales, we made pumps, motors and engines; a huge variety of products. By the 1960s-70s, the company was really only making engines. I think about the legacy that I would like to be able to leave is one, there’s a clear focus on the customer that we have, the United States Navy and the United States Coast Guard, this legacy of defense, enabling freedom of the seas, how important that is.
And second is going back to the original mission of Fairbanks Morse. We’re much more than just an engine company. We now have a motor company, we have a valve company, we have an elevator company, we have all of this other capability that we’ve gone back to be able to add, to say, just almost like the company that existed more than 100 years ago. And so, it’s a little bit of back to our original roots, and I think that whoever gets this job after me, whenever that may be, hopefully they can continue to grow and expand on that in a similar manner to what we’ve been able to do for the last couple of years.
Watch the full Maritime Matters Podcast here:





































