The Path to Zero: First Wave of Ships Explore Green Hydrogen
While there is no consensus on what will be the maritime 'fuel of the future', developers across the world are for the first time testing the use of hydrogen to power ships as the maritime industry races to find technologies to cut emissions and confidence grows the fuel is safe to use commercially.
To reach goals for the shipping industry set by the United Nations, industry leaders say the first net-zero ships must enter the global fleet by 2030. Ships powered by green hydrogen could help meet the target.
Made from electrolysis to split water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity from renewable energy, green hydrogen is emissions free.
Oil major Royal Dutch Shell last month reiterated its commitment to hydrogen, which it saw as "advantaged over other potential zero-emissions fuels for shipping".
While hydrogen's green credentials make it attractive to industrial users, including ship owners and oil majors, it is far less dense than other fuels, meaning more onboard fuel storage capacity is needed. That makes it more feasible, for now, for use in vessels on short voyages.
"(Hydrogen) is going to be massive," said Steve Hall, Chief Executive, Society for Underwater Technology, in a recent interview with Marine Technology Reporter. "Whether it be blue hydrogen, the hydrogen that's being derived from natural gas, and then you capture the carbon and put it back into the rocks, or whether it's the green hydrogen, hydrogen that's been electrolyzed from sea water using renewable electricity."
"And I suspect that by the time we get to 2030 the offshore hydrogen industry is going to be massive (too)," said Hall. "Hydrogen, I think, is going to be key to being able to decarbonize things like locomotives, ships, trucks, for example. The small private automobile is going to be fine running on batteries, but fuel cells is where it's going to be at for large-scale, heavy duty use."
ABB is working on hydrogen fuel cell systems, including for passenger and cargo ships. One of its projects involves developing a fuel cell-based power and propulsion system for a new-build river vessel along France's Rhone river.
"ABB sees short-distance shipping as the first adopters of the fuel cell technology," said Juha Koskela, division president, ABB Marine & Ports.
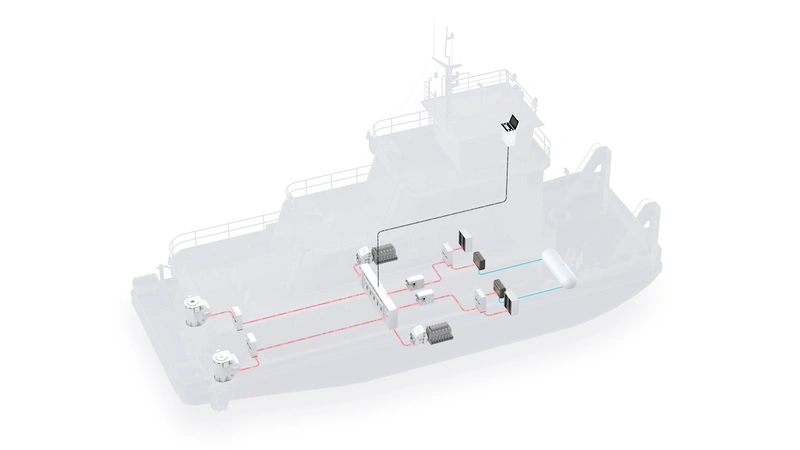 Concept illustration of a push boat powered by fuel cell system (Image: ABB)
Concept illustration of a push boat powered by fuel cell system (Image: ABB)
Fuel system pilots
Green hydrogen fuel costs around 4-8 times the price of very low sulfur fuel oil, estimates by risk management firm DNV GL find.
Other types of hydrogen are cheaper, but that is because they are produced using fossil fuel, which means they are not emissions free.
Green hydrogen is expected to fall in price over the next couple of decades as the cost of renewable energy and electrolyzers falls.
For companies to invest en masse, however, the associated infrastructure for refueling and transportation, including electrolyzers, compressors, storage, tanks and pipelines, must also be in place.
Christos Chryssakis, of DNV GL, said it took around 20 years to establish liquefied natural gas refueling infrastructure. He said the process could be quicker for hydrogen, but industry estimates find many billions in investment would be needed.
In Norway, regulations could accelerate the process.
Cruise ships and ferries sailing through the country's heritage-protected fjords must be emissions-free by 2026, which is prompting shipping companies to consider fuel combinations including hydrogen.
Norwegian-headquartered ship designer and ship yard Ulstein is working on building a support ship for the offshore oil sector that would use hydrogen as one power option.
"Rather than wait for hydrogen bunker infrastructure to be matured, we went for a hybrid design using a containerized solution for the hydrogen storage tanks," Ulstein's Nick Wessels said.
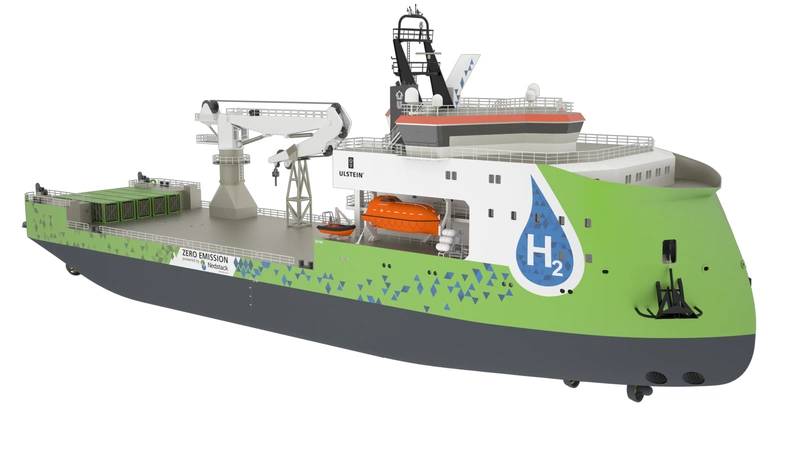 The ULSTEIN SX190 Zero Emission DP2 construction support vessel is Ulstein’s first hydrogen powered offshore vessel, featuring a Nedstack fuel cell power system. The DP2 vessel can cater for a large variety of offshore support operations. (Image: Ulstein)
The ULSTEIN SX190 Zero Emission DP2 construction support vessel is Ulstein’s first hydrogen powered offshore vessel, featuring a Nedstack fuel cell power system. The DP2 vessel can cater for a large variety of offshore support operations. (Image: Ulstein)
The company is also working on a separate hydrogen project for wind installation turbine vessels, he said.
Municipalities in Norway have launched a tender process, which includes the development of hydrogen-powered, high-speed vessels by 2022, officials say.
Other countries are also making strides. Belgium's Compagnie Maritime Belge (CMB) built its first hydrogen-powered passenger shuttle boat, which hit the waters in 2017 in Belgium. It will provide a hydrogen ferry for Japan by April next year - the first hydrogen ferry in Asia - and is involved in a tug boat project with the port of Antwerp, CMB's chief executive Alexander Saverys said.
Other ports are working on hydrogen options at terminals. The Spanish port of Valencia said it will deploy prototype machinery, including for box container handling operations, early in 2021, while Britain's Felixstowe port is looking into hydrogen, based on its proximity to offshore wind farms and a nuclear power plant.
Short trips versus ocean trade
The shipping industry, which is responsible for 2.89% of global CO2 emissions, is in the midst of a transition to fuels that would reduce those emissions by 50% by 2050 from 2008 levels.
A study by the non-profit Global Maritime Forum (GMF), which mapped out 66 projects looking at zero emissions in shipping, showed 19 of the 21 initiatives relating to fuel production used hydrogen in some form.
The majority of these anticipated using hydrogen to make other products, such as ammonia, methanol or ethanol, to improve the schemes' viability. Seven are pure hydrogen projects.
Some in the shipping industry remain unconvinced hydrogen is safe as a power source for larger vessels carrying large amounts of fuel onboard.
But for many, the bigger question is economics.
"The big challenge using hydrogen for deep sea shipping is the cargo volume you would lose to have enough hydrogen stored for long voyages, which could be a commercial killer," Kasper Søgaard, GMF head of research, said.
Ulstein's Wessels expects the need for backup fuel options will persist until there leap in technology and infrastructure.
"I don’t think you can build a completely hydrogen-powered vessel of large size at this point in time. There will still need to be another accessible power source like diesel," he said.
(Reuters)