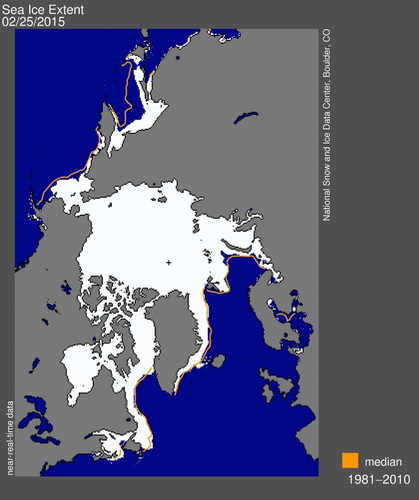
Arctic sea ice has set a new winter record by freezing over the smallest extent since satellite records began in 1979, in a new sign of long-term climate change, U.S. data showed on Thursday.
The ice floating on the Arctic Ocean around the North Pole reached its maximum annual extent of just 14.54 million square kms (5.61 million sq miles) on Feb. 25 - slightly bigger than Canada - and is now expected to shrink with a spring thaw.
"This year's maximum ice extent was the lowest in the satellite record, with below-average ice conditions everywhere except in the Labrador Sea and Davis Strait," the U.S. National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) said in a statement.
A late season surge in ice was still possible, it said. The ice was 1.1 million sq kms smaller than the 1981-2010 average, and below the previous lowest maximum in 2011.
With the return of the sun to the Arctic after months of winter darkness, the ice shrinks to a minimum in September.
The U.N. panel of climate scientists links the long-term shrinkage of the ice, by 3.8 percent a decade since 1979, to global warming and says Arctic summertime sea ice could vanish in the second half of the century.
"The majority of models point in the same direction - less ice," said Sebastian Gerland, an expert at the Norwegian Polar Institute. And he said far less ice was surviving more than one winter - such ice is often thickest and most resilient.
The U.N.'s World Meteorological Organization says 2014 was the warmest year since records began in the 19th century. Almost 200 nations have agreed to work out a deal in December in Paris to slow global warming.
The Arctic thaw is disrupting indigenous hunting lifestyles in the Arctic while making the region more accessible. But low oil prices have discouraged exploration and tensions between the West and Russia have limited interest in Arctic shipping.
"This new data on sea ice loss sends a clear message to the global community that the Arctic is unravelling, warming twice as fast as the rest of the planet," Rafe Pomerance, chair of Arctic 21, a group of environmental groups, said in a statement.
At the other end of the planet, the NSIDC said earlier this month that sea ice around Antarctica was the fourth-smallest for summer. Climate scientists say the apparently contradictory trend may be tied to changing winds and currents.
(Reporting by Alister Doyle; Editing by Tom Heneghan and Susan Fenton)